
Key Points:
- High-functioning autism refers to individuals with autism who can manage many aspects of daily life independently but still face challenges.
- Symptoms of high-functioning autism can include difficulty with social interactions, repetitive behaviors, and a strong preference for routine.
- Early diagnosis and targeted therapies, such as ABA, can help individuals manage challenges and improve social skills, communication, and daily functioning.
When it comes to autism, many people often hear the term “high-functioning autism” and wonder what it really means. High-functioning autism refers to individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) who have average or above-average intellectual abilities but still struggle with social interactions and behavior regulation.
According to research, about 40 to 50% of autistic children have problems with both emotions and behavior. In fact, the challenges of high-functioning autism can sometimes be harder to spot, which may make it more difficult for people to get the help they need.
In this article, we will explore the symptoms, diagnosis, and effective management strategies for individuals with high-functioning autism. This information is important not only for understanding the condition better but also for parents and caregivers seeking the right interventions and support for their loved ones. The aim is to help those with high-functioning autism live fulfilling and independent lives.
What Are the Symptoms of High-Functioning Autism?
The symptoms of high-functioning autism can often be subtle but are still noticeable when individuals interact with others or experience change. It’s essential to understand that while people with high-functioning autism may not have significant cognitive impairments, they still face significant challenges in social communication and behavior.
Here are some symptoms of high-functioning autism:
1. Social Communication Difficulties:
Individuals with high-functioning autism may struggle with interpreting social cues such as body language, tone of voice, and facial expressions. These individuals might not recognize when someone is upset, and they may miss subtle clues in a conversation that indicates when to speak or remain quiet. This can lead to misunderstandings or awkward social interactions, even though the individual may want to connect with others.
2. Restricted Interests and Repetitive Behaviors:
Individuals with high-functioning autism often experience a deep, intense focus on a specific subject or hobby. While having strong interests can be a positive trait, it can sometimes interfere with socializing, especially when the individual only wants to talk about their area of focus.
Additionally, repetitive behaviors like hand-flapping, rocking, or repeating certain phrases may also be present, although these behaviors may be less pronounced than in other forms of autism.
3. Sensitivity to Sensory Input:
Many individuals with high-functioning autism are more sensitive to sensory experiences. For example, they might be particularly sensitive to certain textures, smells, or sounds. This heightened sensory sensitivity can make certain environments overwhelming and uncomfortable.
4. Difficulty with Change and Transitions:
Individuals with high-functioning autism often thrive in structured, predictable environments. Any significant change—whether it’s a shift in routine, unexpected events, or new environments—can cause anxiety or distress. These challenges can make it hard for individuals with high-functioning autism to adapt to changes in school, work, or home life.
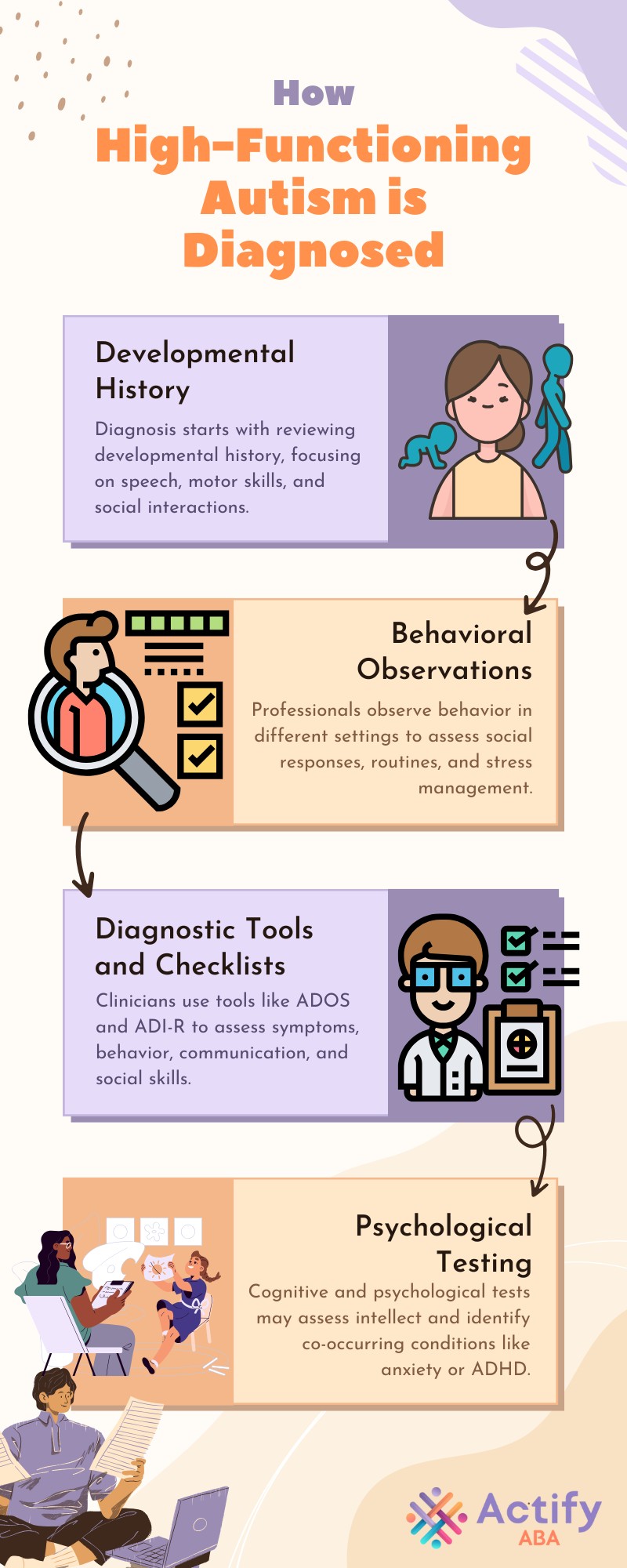
How Can High-Functioning Autism Be Managed?
While there is no cure for autism, several treatments and strategies can help individuals manage the symptoms and improve their quality of life. Early intervention and ongoing support are essential for long-term success.
1. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA):
ABA is one of the most widely used and effective therapies for autism. It focuses on teaching positive behaviors while reducing unwanted behaviors. ABA can be tailored to the individual’s unique needs, helping them develop crucial skills in communication, socialization, and self-regulation. For individuals with high-functioning autism, ABA therapy can provide the tools necessary to navigate social interactions and cope with sensory sensitivities.
2. Social Skills Training:
Social skills training teaches individuals with high-functioning autism how to interact appropriately with others. This might include learning how to start a conversation, make eye contact, and understand social cues. Role-playing, peer interactions, and video modeling are common techniques used in social skills training.
3. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
CBT helps individuals with high-functioning autism manage anxiety, depression, and stress. By identifying negative thought patterns and teaching coping mechanisms, CBT empowers individuals to handle social anxiety, sensory overload, and changes in routine. It’s particularly beneficial for those who may have co-occurring mental health conditions like anxiety disorders.
4. Speech Therapy:
Speech therapy can assist with communication difficulties by focusing on articulation, language comprehension, and non-verbal communication. This therapy is beneficial for those who need support in expressing themselves more clearly or understanding others’ communication.
5. Occupational Therapy (OT):
OT helps individuals with high-functioning autism address sensory processing issues, motor coordination difficulties, and daily living skills. For example, OT may help improve the individual’s ability to perform tasks like dressing, cooking, or managing sensory overload. This therapy is critical for fostering independence and improving quality of life.
Tips for Managing High-Functioning Autism at Home
Managing high-functioning autism at home can present unique challenges, but with the right strategies, it is possible to create a supportive environment that promotes growth and well-being.
1. Establish Routines:
People with high-functioning autism often thrive in structured environments. Establishing and sticking to daily routines helps reduce anxiety and provide a sense of predictability. Clear schedules for meals, bedtime, and activities can help manage transitions and minimize stress.
2. Minimize Sensory Overload:
At home, try to create a sensory-friendly environment that helps reduce overwhelming stimuli. This may involve dimming lights, using noise-canceling headphones, or providing tactile objects for calming. Ensuring a quiet, calm space can help the individual relax and feel safe.
3. Use Clear Communication:
When communicating with someone with high-functioning autism, it’s important to be clear, concise, and direct. Avoid ambiguous language or sarcasm, and give them time to process what you’ve said. Visual aids or written instructions can also be helpful.
4. Encourage Interests and Strengths:
Individuals with high-functioning autism may have deep interests in specific topics. Encouraging these interests can build confidence, promote learning, and provide opportunities for social connection. Helping them engage with others who share similar interests can also foster positive social interactions.

How to Support Your Child with High-Functioning Autism
Supporting a child with high-functioning autism means recognizing their individual needs and offering encouragement in a way that respects their unique perspective. Here are some updated strategies for effective support:
1. Be patient and flexible
Children with high-functioning autism can be very detail-oriented and may have rigid thinking patterns. Be patient as they process changes and encourage flexibility in their thinking over time.
2. Encourage social skills development.
Social interactions can be difficult. Support your child by practicing role-playing exercises at home to help them understand social cues and appropriate responses.
3. Use positive reinforcement
Celebrate small victories and progress, whether it’s mastering a new task or simply coping well in a challenging situation. Positive reinforcement boosts self-esteem and motivates them to keep trying.
4. Limit distractions
Create an environment where your child can focus. Whether it’s for homework or relaxing a quiet, clutter-free space can help them manage distractions and reduce anxiety.
5. Support emotional regulation
High-functioning autism often comes with challenges in managing emotions. Help your child recognize and express their feelings, and teach coping strategies like deep breathing or using fidget tools.
By adapting to your child’s specific needs, you’ll foster an environment where they can thrive both at home and in the wider world.
ABA Therapy in Maryland – Helping Manage High-Functioning Autism
If you are looking for effective ways to manage high-functioning autism, Actify offers ABA therapy in Maryland. Our team is experienced in providing tailored treatment plans that support individuals with autism in developing crucial social, communication, and adaptive skills. A
BA therapy is a proven method for helping individuals with high-functioning autism lead fulfilling lives. Contact us today to learn more about how our ABA therapy programs can make a difference in managing autism and improving quality of life.
