
Key Points:
- Attention-seeking behavior is common in children, especially those with autism, and can disrupt learning and social development.
- ABA therapy identifies why these behaviors occur and uses evidence-based strategies to replace them with appropriate actions.
- Parents can support progress by reinforcing positive behaviors and avoiding unintentional reinforcement of negative ones.
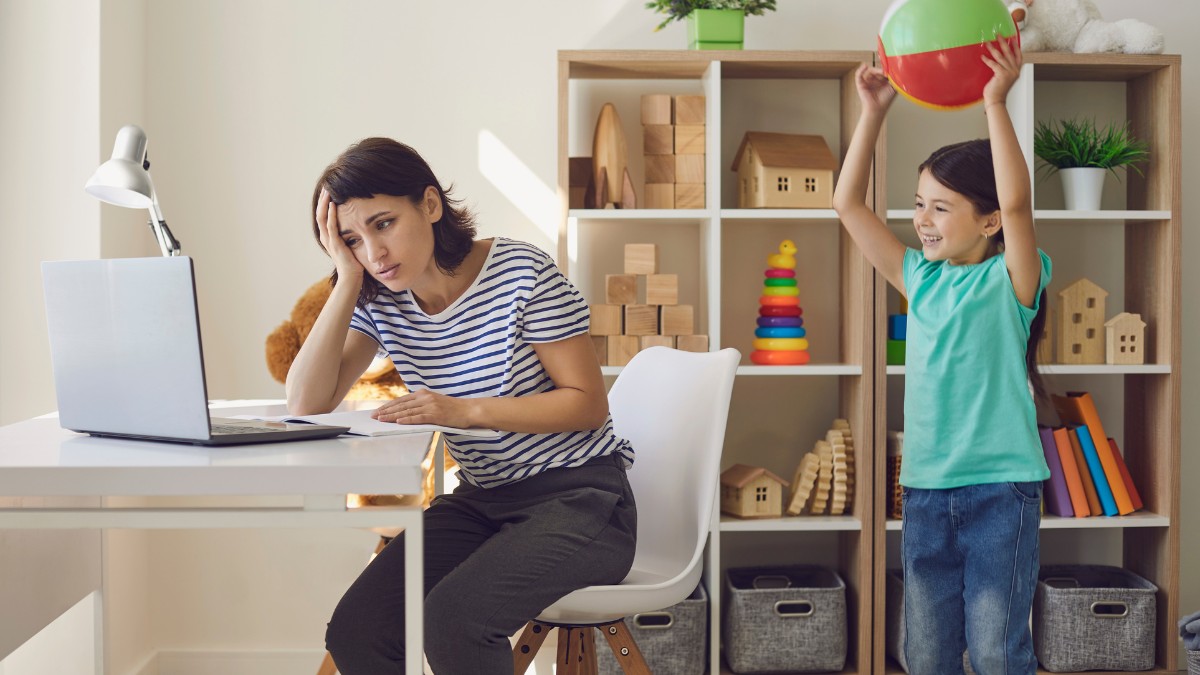
Imagine a child constantly acting out—talking over others, making loud noises, or throwing things. To an outsider, it might seem like defiance, but often, it’s a cry for connection. Many children engage in attention-seeking behavior simply because they don’t know how to express their needs appropriately. ABA therapy helps replace disruptive behaviors with effective communication and social skills.
What is Attention-Seeking Behavior in ABA?
Attention-seeking behavior in ABA refers to any action a child engages in to gain attention from others. This can be positive (e.g., asking for help) or disruptive (e.g., tantrums or yelling).
Common examples include:
- Calling out in class or interrupting conversations.
- Engaging in repetitive behaviors like tapping or making noises.
- Throwing objects, crying, or displaying aggressive behavior.
Not all attention-seeking behaviors are problematic, but when they interfere with daily activities or social interactions, intervention is necessary.
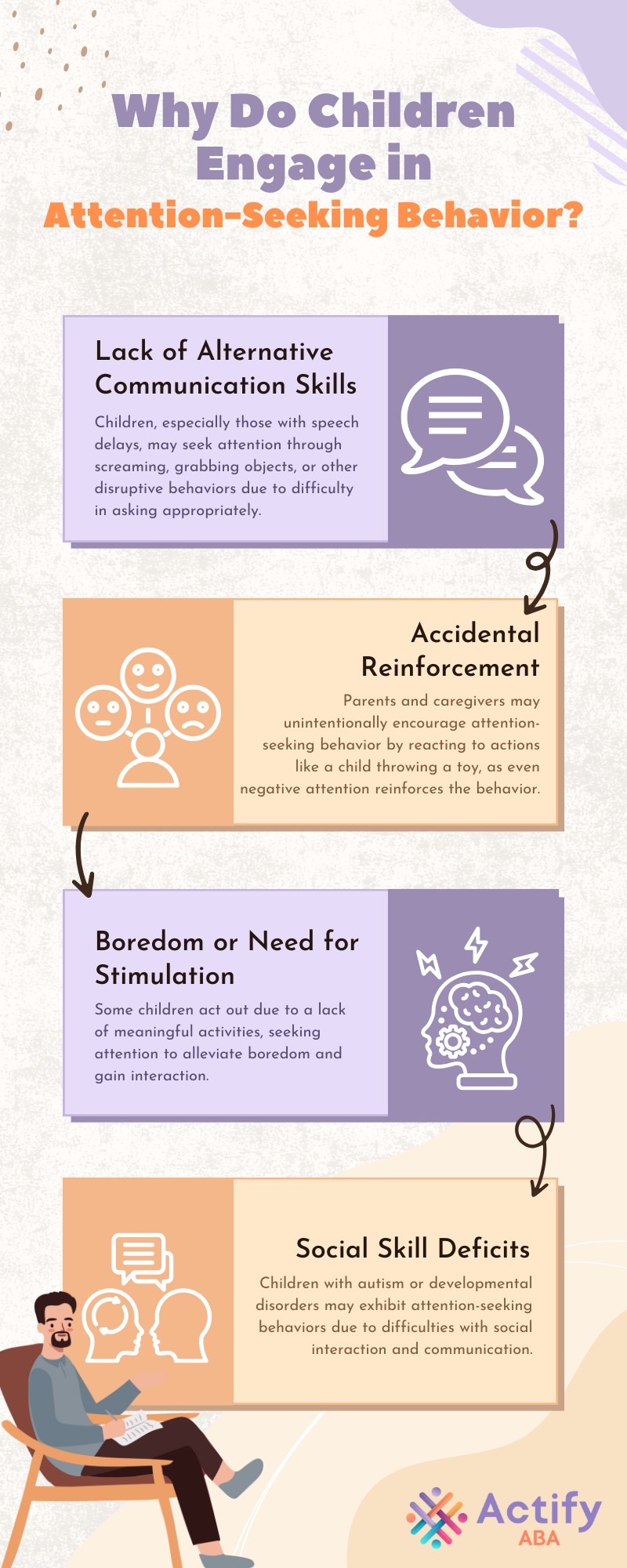
Children seek attention because it is a fundamental human need. However, when they struggle with communication or social skills, they may resort to inappropriate methods to get noticed. Several factors contribute to this behavior:
How Does ABA Therapy Address Attention-Seeking Behavior?
ABA therapy focuses on understanding the function of a behavior and replacing it with more appropriate actions. This approach helps children learn positive ways to seek attention without engaging in disruptive behavior.
1. Identifying the Function of the Behavior
ABA therapists conduct a functional behavior assessment (FBA) to determine why the behavior occurs. This includes:
- Observing when and where the behavior happens.
- Identifying triggers and consequences.
- Analyzing patterns to determine if the behavior is attention-seeking.
2. Teaching Alternative Behaviors
Once the function is identified, ABA therapy teaches children replacement behaviors that serve the same purpose in a more appropriate way. Examples include:
- Teaching a child to raise their hand instead of shouting in class.
- Encouraging verbal requests or sign language instead of physical outbursts.
- Using social stories or role-playing to model appropriate attention-seeking behaviors.
3. Reinforcing Positive Behavior
Positive reinforcement plays a key role in ABA therapy. When a child engages in appropriate behavior, they receive immediate and meaningful reinforcement such as praise, stickers, or access to a favorite activity. This strengthens the likelihood of them repeating the desired behavior.
4. Reducing Reinforcement for Negative Behaviors
ABA therapy also helps caregivers respond strategically to negative attention-seeking behaviors. Strategies include:
- Planned ignoring: Not reacting to behaviors like whining or interrupting.
- Redirection: Guiding the child toward a more appropriate activity.
- Differential reinforcement: Rewarding positive behaviors while withholding reinforcement for negative ones.
By consistently applying these techniques, children learn that positive behaviors are more effective in gaining attention than disruptive ones.

Common ABA Strategies for Managing Attention-Seeking Behavior
Addressing attention-seeking behavior requires consistency and patience. ABA therapy employs a variety of strategies to support behavior change.
1. Differential Reinforcement of Alternative Behavior (DRA)
This technique involves reinforcing a positive behavior that serves the same function as the negative one. For example:
- If a child frequently screams for attention, they are taught to use a simple phrase like “Look at me” instead. When they use words instead of screaming, they receive immediate praise.
2. Extinction
Extinction involves removing reinforcement for undesired behaviors. If a child repeatedly interrupts and receives attention each time, a therapist may instruct caregivers to ignore the behavior. Over time, the child learns that interrupting no longer gets them what they want.
3. Noncontingent Attention (NCA)
Some children act out because they feel ignored. By providing regular attention at set intervals, ABA therapy helps reduce disruptive behaviors caused by seeking attention. Examples include:
- Giving a child a few minutes of one-on-one interaction every 10 minutes.
- Engaging in brief, positive interactions before the child seeks attention inappropriately.
4. Functional Communication Training (FCT)
FCT teaches children how to appropriately request attention using words, gestures, or assistive communication devices. This approach is particularly useful for nonverbal children or those with speech delays.
How Can Parents Support ABA Strategies at Home?
Parents play a key role in ensuring that ABA techniques are effective beyond therapy sessions. Consistency at home helps children learn and apply new behaviors in daily life. Here are practical ways to support their progress:
Demonstrate and Reinforce Positive Attention-Seeking Behaviors
Children learn by example, so it’s important to model appropriate ways to ask for attention. Show them how to use words, gestures, or a tap on the shoulder instead of yelling or interrupting. When they use these positive behaviors, immediately acknowledge and praise their effort. This reinforces the idea that appropriate ways of seeking attention are more effective.
Minimize Attention to Disruptive Behaviors
Reacting strongly to negative attention-seeking behavior—whether with frustration or immediate engagement—can unintentionally encourage it. Instead, stay calm and avoid reinforcing actions like whining or excessive interruptions. If possible, ignore minor misbehaviors and instead guide your child toward a more constructive way to communicate their needs.
Offer Regular, Intentional Attention
Many attention-seeking behaviors stem from a child feeling overlooked. To prevent this, provide frequent, scheduled interactions throughout the day. Spend quality time engaging in activities they enjoy, such as reading, playing, or talking. Proactively offering attention before negative behaviors emerge helps reduce the need for them to act out.
Maintain Consistency Across Caregivers
Children thrive on consistency, so it’s crucial that all caregivers—including parents, teachers, and therapists—follow the same approach. If one person reinforces negative behaviors while another ignores them, it can create confusion. Work closely with ABA professionals to establish clear, consistent responses to both positive and negative attention-seeking actions.
Partner with Actify to Support Your Child’s Growth
Managing attention-seeking behavior with ABA therapy requires patience, consistency, and expert guidance. By understanding why these behaviors occur and reinforcing positive alternatives, children can develop healthier ways to seek interaction and connection.
If your child struggles with attention-seeking behaviors, Actify can help. Our dedicated team provides individualized ABA therapy designed to build essential communication and social skills. Whether at home, in school, or within the community, we offer the support your child needs to thrive.
We proudly serve families in Maryland and surrounding areas. Contact us today to learn how ABA therapy can help your child develop positive behavior patterns and meaningful connections.
